Chapter 11 MI50: Ordered exploitation results
Here we present the results for best performances found by each selection scheme replicate on the ordered exploitation diagnostic with configurations presented below. Best performance found refers to the largest average trait score found in a given population. Note that performance values fall between 0.0 and 100.0. For our the configuration of these experiments, we execute migrations every 50 generations and there are 4 islands in a ring topology. When migrations occur, we swap two individuals (same position on each island) and guarantee that no solution can return to the same island.
11.2 Truncation selection
Here we analyze how the different population structures affect truncation selection (size 8) on the ordered exploitation diagnostic.
11.2.1 Performance over time
lines = filter(mi50_over_time, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TRUNCATION') %>%
group_by(Structure, Generations) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
min = min(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
mean = mean(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
max = max(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY
)
ggplot(lines, aes(x=Generations, y=mean, group = Structure, fill = Structure, color = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = min, ymax = max), alpha = 0.1) +
geom_line(size = 0.5) +
geom_point(data = filter(lines, Generations %% 2000 == 0), size = 2.5, stroke = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average trait score",
limits=c(-1, 101),
breaks=seq(0,100, 20),
labels=c("0", "20", "40", "60", "80", "100")
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(0, 50000),
breaks=c(0, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000),
labels=c("0e+4", "1e+4", "2e+4", "3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4")
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle("Performance over time") +
p_theme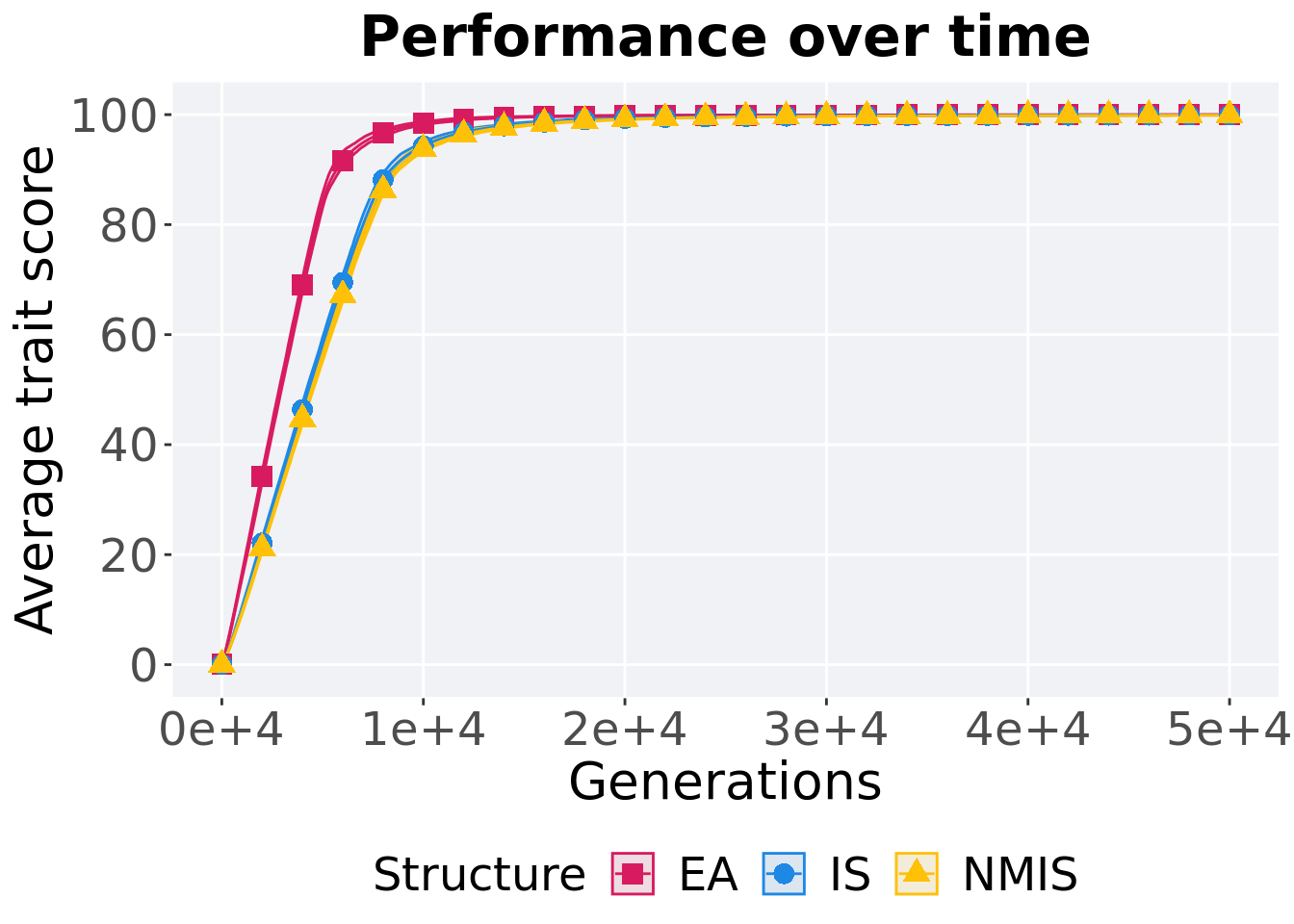
11.2.2 Generation satisfactory solution found
First generation a satisfactory solution is found throughout the 50,000 generations.
filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TRUNCATION') %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = Structure, y = Generations , color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = .1), size = 1.5, alpha = 1.0) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .2, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Generation"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Structure"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Generation satisfactory solution found')+
p_theme + coord_flip()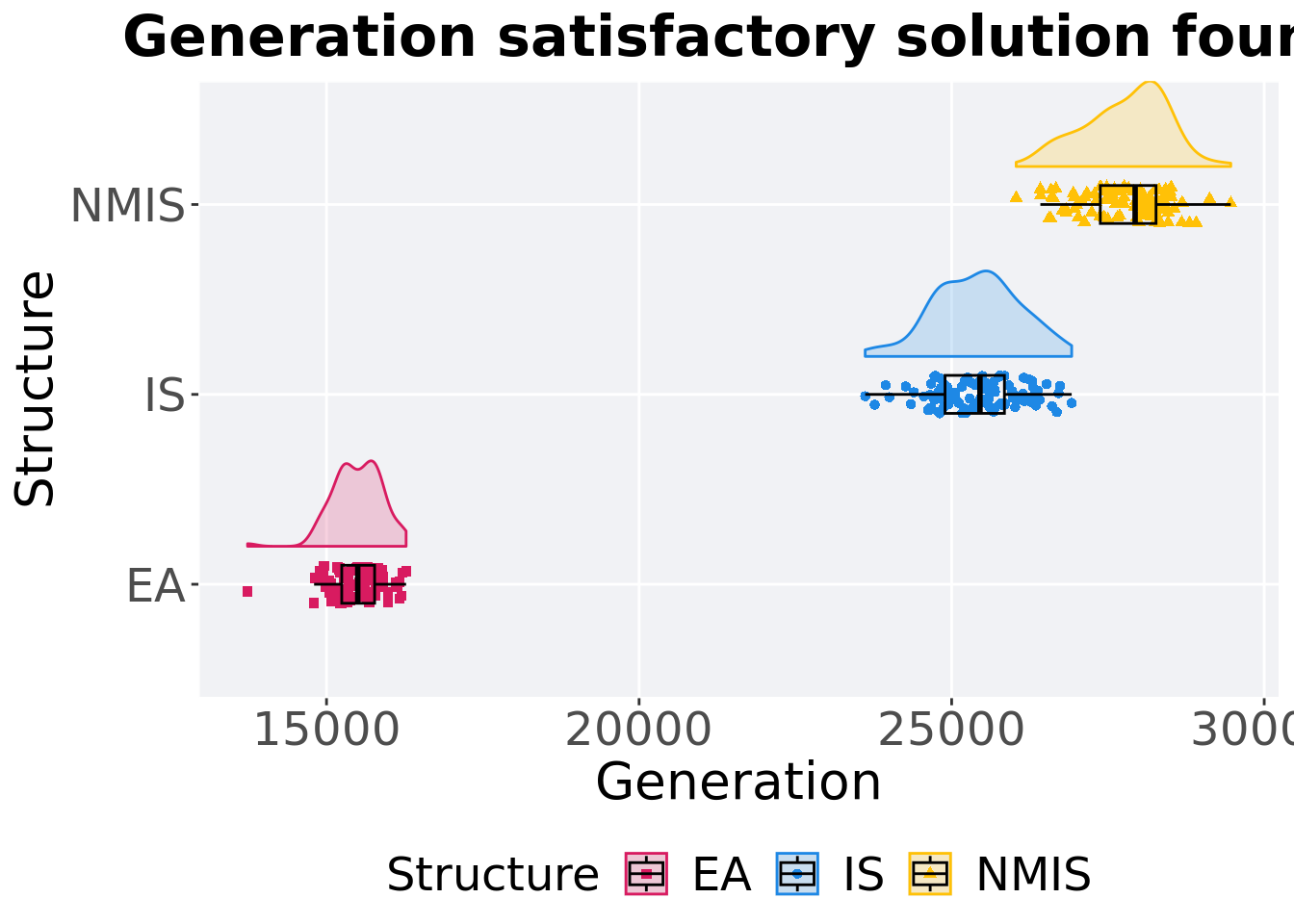
11.2.2.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the first generation a satisfactory solution is found.
ssf = filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TRUNCATION' & Generations < 60000)
ssf %>%
group_by(Structure) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(Generations)),
min = min(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(Generations, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 3 x 8
## Structure count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 EA 100 0 13737 15500. 15493. 16273 526.
## 2 IS 100 0 23617 25453 25405. 26920 950
## 3 NMIS 100 0 26032 27935 27781. 29465 892.Kruskal–Wallis test provides evidence of difference among selection schemes.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: Generations by Structure
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 264.17, df = 2, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = ssf$Generations, g = ssf$Structure, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'g')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: ssf$Generations and ssf$Structure
##
## EA IS
## IS <2e-16 -
## NMIS <2e-16 <2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni11.3 Tournament selection
Here we analyze how the different population structures affect tournament selection (size 8) on the ordered exploitation diagnostic.
11.3.1 Performance over time
lines = filter(mi50_over_time, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TOURNAMENT') %>%
group_by(Structure, Generations) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
min = min(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
mean = mean(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
max = max(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY
)
ggplot(lines, aes(x=Generations, y=mean, group = Structure, fill = Structure, color = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = min, ymax = max), alpha = 0.1) +
geom_line(size = 0.5) +
geom_point(data = filter(lines, Generations %% 2000 == 0), size = 2.5, stroke = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average trait score",
limits=c(-1, 101),
breaks=seq(0,100, 20),
labels=c("0", "20", "40", "60", "80", "100")
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(0, 50000),
breaks=c(0, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000),
labels=c("0e+4", "1e+4", "2e+4", "3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4")
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle("Performance over time") +
p_theme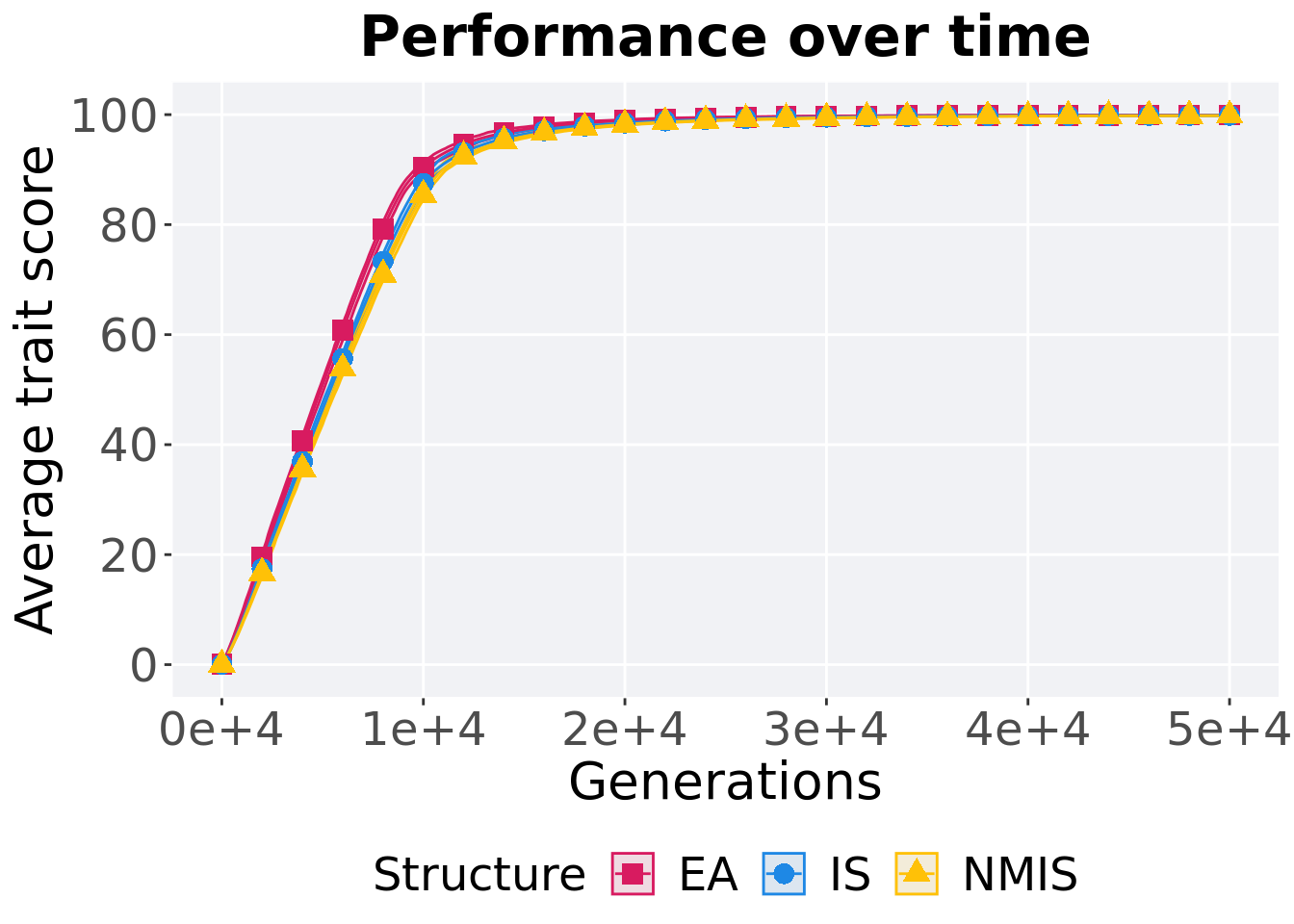
11.3.2 Generation satisfactory solution found
First generation a satisfactory solution is found throughout the 50,000 generations.
filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TOURNAMENT') %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = Structure, y = Generations , color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = .1), size = 1.5, alpha = 1.0) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .2, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Generation"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Structure"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Generation satisfactory solution found')+
p_theme + coord_flip()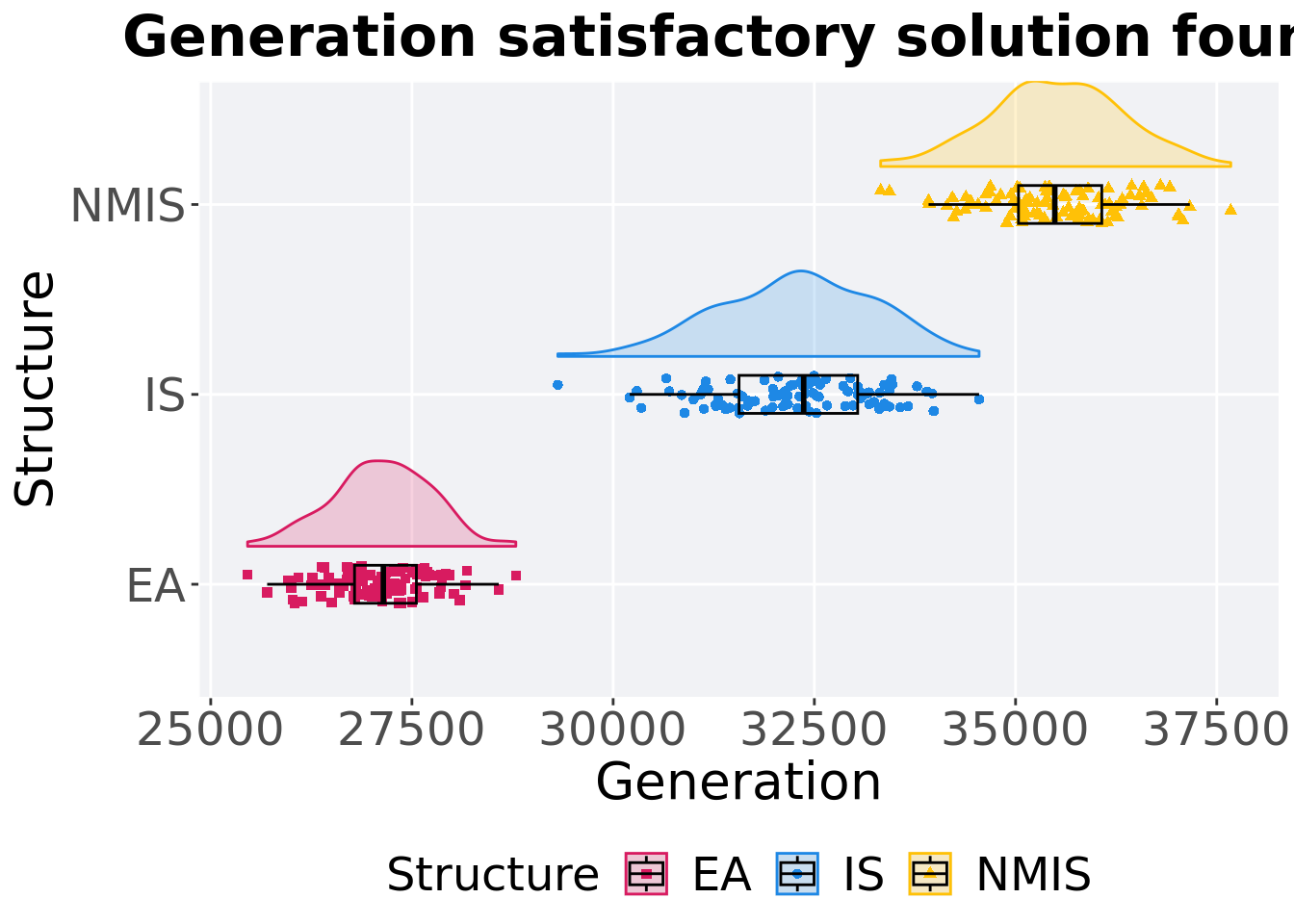
11.3.2.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the first generation a satisfactory solution is found.
ssf = filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'TOURNAMENT' & Generations < 60000)
ssf %>%
group_by(Structure) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(Generations)),
min = min(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(Generations, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 3 x 8
## Structure count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 EA 100 0 25458 27144. 27124. 28791 769.
## 2 IS 100 0 29313 32368. 32281. 34547 1474
## 3 NMIS 100 0 33324 35488. 35510. 37674 1035.Kruskal–Wallis test provides evidence of difference among selection schemes.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: Generations by Structure
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 264.58, df = 2, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = ssf$Generations, g = ssf$Structure, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'g')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: ssf$Generations and ssf$Structure
##
## EA IS
## IS <2e-16 -
## NMIS <2e-16 <2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni11.4 Lexicase selection
Here we analyze how the different population structures affect standard lexicase selection on the ordered exploitation diagnostic.
11.4.1 Performance over time
lines = filter(mi50_over_time, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE') %>%
group_by(Structure, Generations) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
min = min(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
mean = mean(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY,
max = max(pop_fit_max) / DIMENSIONALITY
)
ggplot(lines, aes(x=Generations, y=mean, group = Structure, fill = Structure, color = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = min, ymax = max), alpha = 0.1) +
geom_line(size = 0.5) +
geom_point(data = filter(lines, Generations %% 2000 == 0), size = 2.5, stroke = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average trait score",
limits=c(-1, 101),
breaks=seq(0,100, 20),
labels=c("0", "20", "40", "60", "80", "100")
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(0, 50000),
breaks=c(0, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000),
labels=c("0e+4", "1e+4", "2e+4", "3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4")
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle("Performance over time") +
p_theme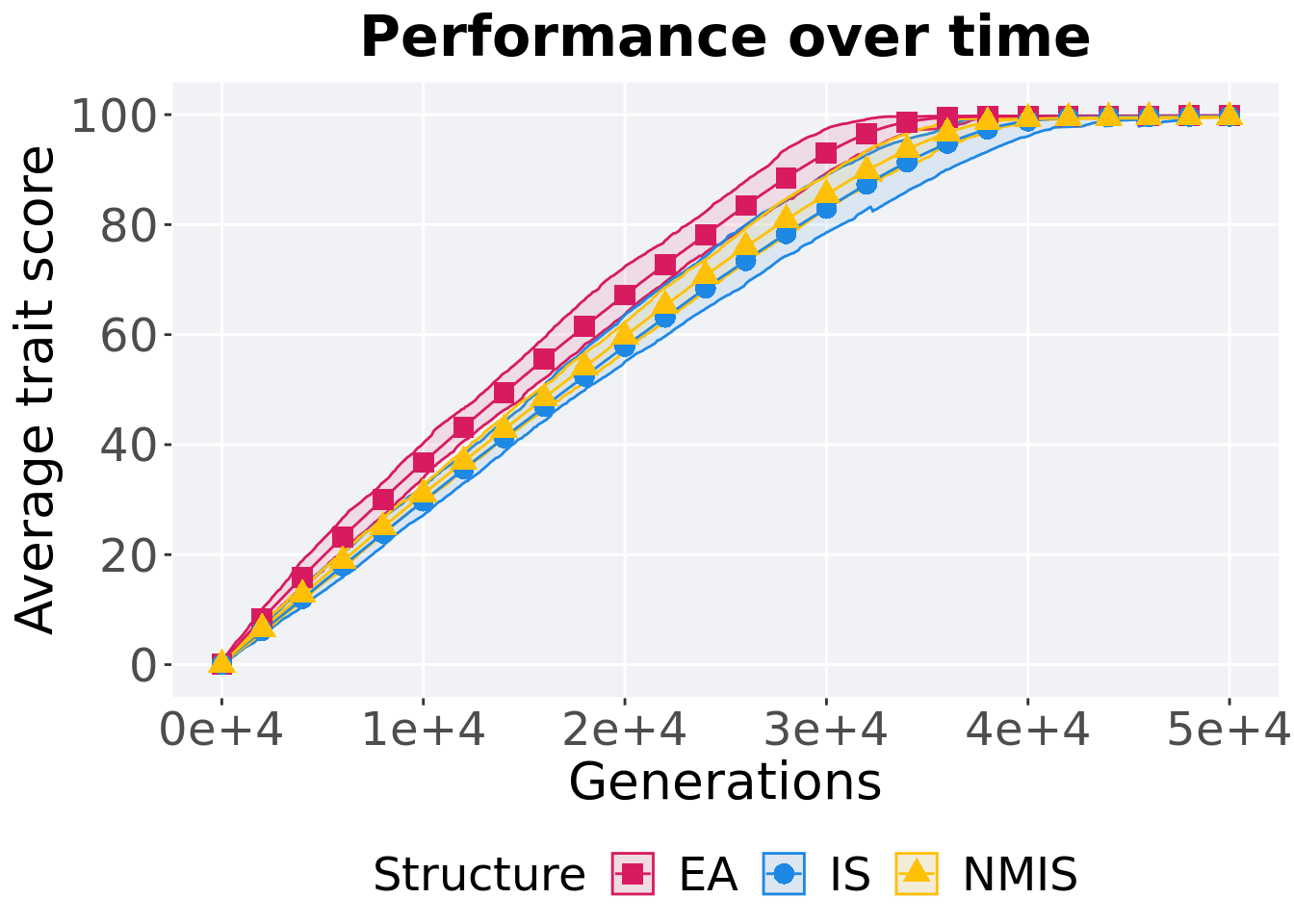
11.4.2 Best performance
First generation a satisfactory solution is found throughout the 50,000 generations.
filter(mi50_best, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & VAR == 'pop_fit_max') %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = Structure, y = VAL / DIMENSIONALITY, color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = .1), size = 1.5, alpha = 1.0) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .2, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average trait score"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Structure"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Best performance')+
p_theme + coord_flip()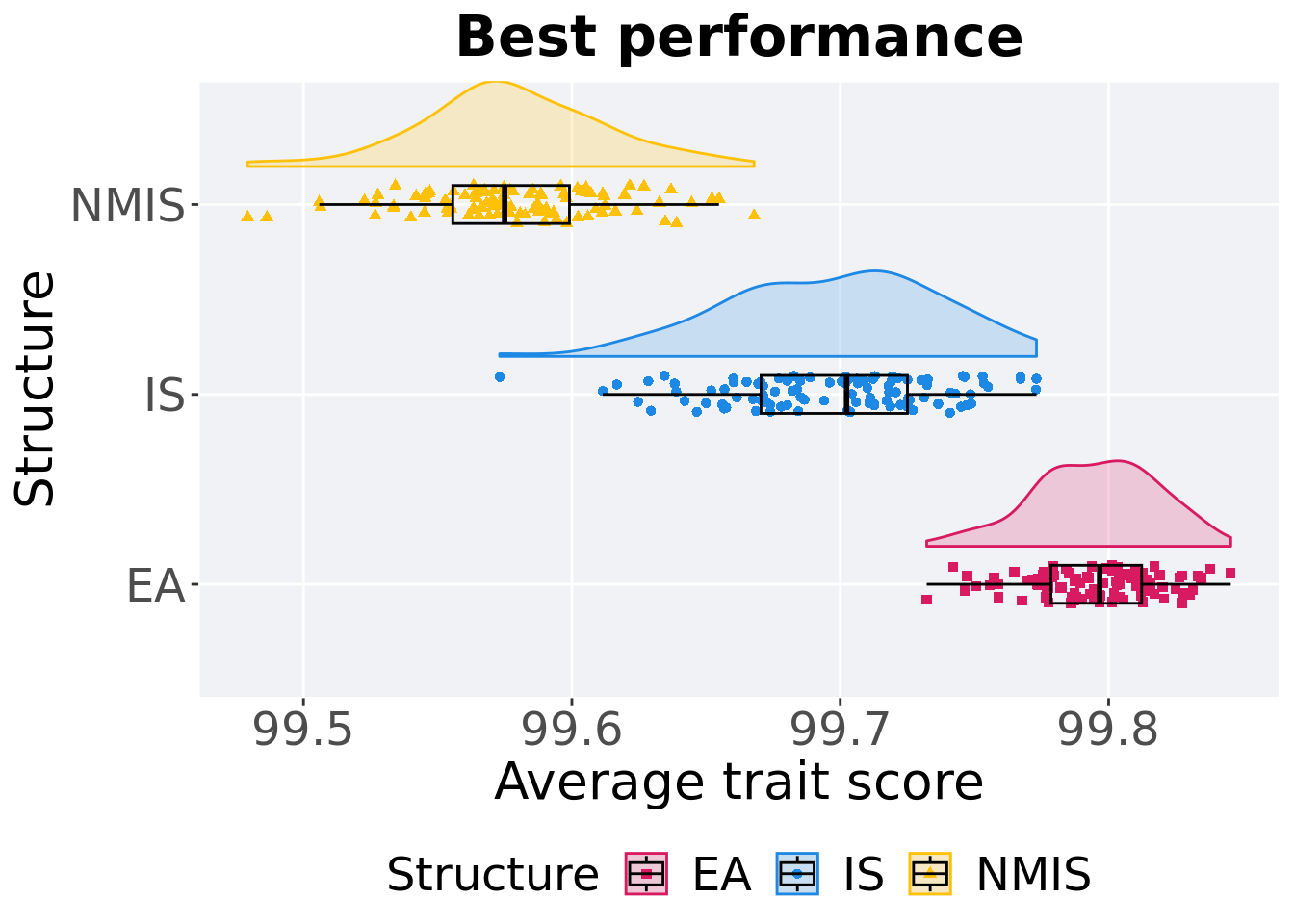
11.4.2.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the first generation a satisfactory solution is found.
performance = filter(mi50_best, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & VAR == 'pop_fit_max')
performance %>%
group_by(Structure) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(VAL)),
min = min(VAL, na.rm = TRUE) / DIMENSIONALITY,
median = median(VAL, na.rm = TRUE) / DIMENSIONALITY,
mean = mean(VAL, na.rm = TRUE) / DIMENSIONALITY,
max = max(VAL, na.rm = TRUE) / DIMENSIONALITY,
IQR = IQR(VAL, na.rm = TRUE) / DIMENSIONALITY
)## # A tibble: 3 x 8
## Structure count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 EA 100 0 99.7 99.8 99.8 99.8 0.0338
## 2 IS 100 0 99.6 99.7 99.7 99.8 0.0545
## 3 NMIS 100 0 99.5 99.6 99.6 99.7 0.0435Kruskal–Wallis test provides evidence of difference among selection schemes.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: VAL by Structure
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 259.68, df = 2, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = performance$VAL, g = performance$Structure, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'l')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: performance$VAL and performance$Structure
##
## EA IS
## IS <2e-16 -
## NMIS <2e-16 <2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni11.4.3 Final performance
First generation a satisfactory solution is found throughout the 50,000 generations.
filter(mi50_over_time, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & Generations == 50000) %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = Structure, y = pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = .1), size = 1.5, alpha = 1.0) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .2, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Average trait score"
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Structure"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Final performance')+
p_theme + coord_flip()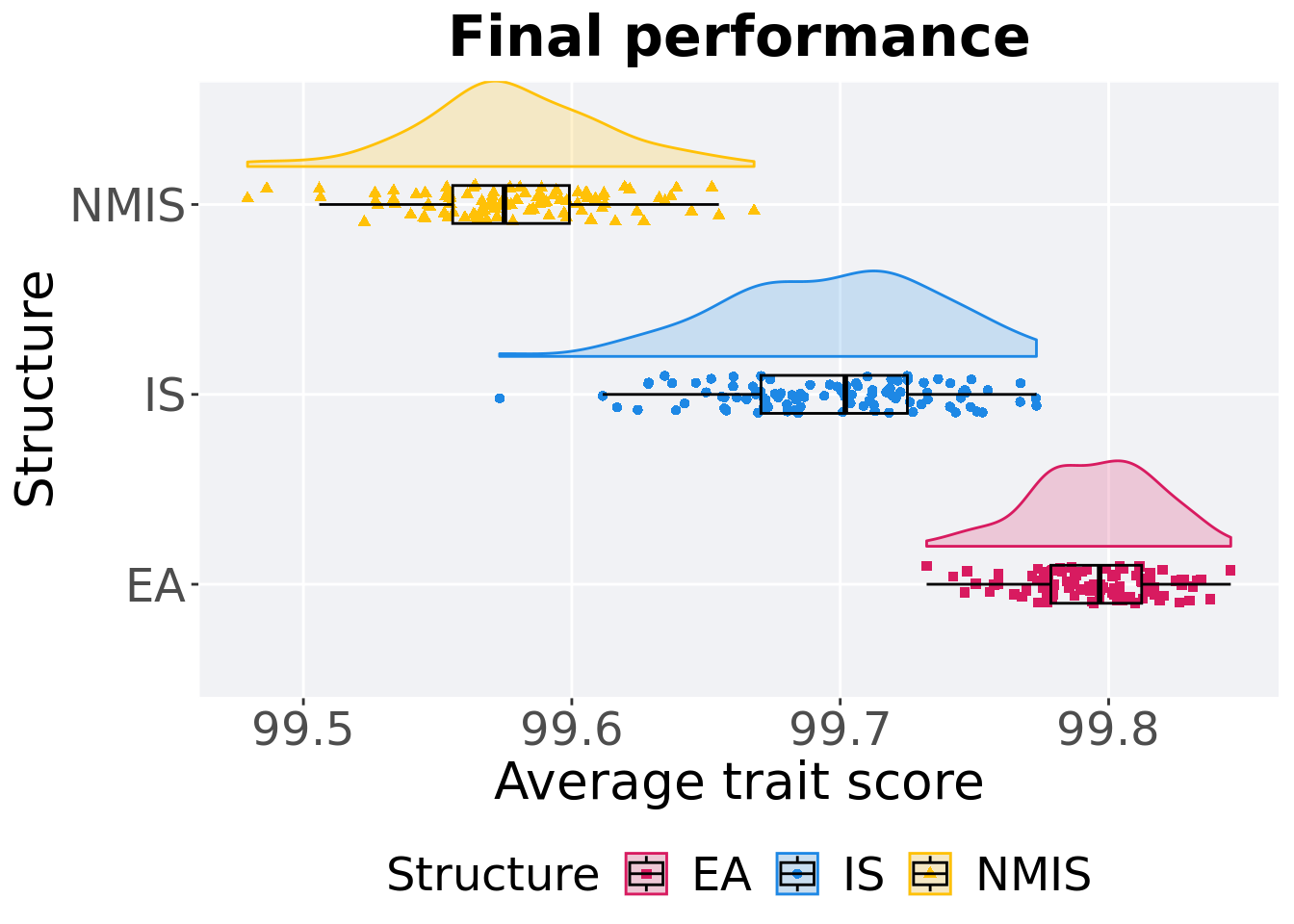
11.4.3.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the first generation a satisfactory solution is found.
performance = filter(mi50_over_time, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & Generations == 50000)
performance %>%
group_by(Structure) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(pop_fit_max)),
min = min(pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(pop_fit_max / DIMENSIONALITY, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 3 x 8
## Structure count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 EA 100 0 99.7 99.8 99.8 99.8 0.0338
## 2 IS 100 0 99.6 99.7 99.7 99.8 0.0545
## 3 NMIS 100 0 99.5 99.6 99.6 99.7 0.0435Kruskal–Wallis test provides evidence of difference among selection schemes.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: pop_fit_max by Structure
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 259.68, df = 2, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = performance$pop_fit_max, g = performance$Structure, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'l')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: performance$pop_fit_max and performance$Structure
##
## EA IS
## IS <2e-16 -
## NMIS <2e-16 <2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni11.4.4 Generation satisfactory solution found
First generation a satisfactory solution is found throughout the 50,000 generations.
lex_fail = filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & GENERATIONS < Generations)
lex_fail$Generations = 55000
lex_fail$Structure <- factor(lex_fail$Structure, levels = MODEL)
filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE'& Generations <= GENERATIONS) %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = Structure, y = Generations, color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .2, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = .1), size = 1.5, alpha = 1.0) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .2, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0) +
geom_point(data = lex_fail, aes(x = Structure, y = Generations, color = Structure, fill = Structure, shape = Structure),position = position_jitter(width = .05), size = 2.5) +
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_y_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(30000, 55000),
breaks=c(30000, 40000, 50000, 55000),
labels=c("3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4", "Fail")
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Structure"
) +
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
p_theme + coord_flip()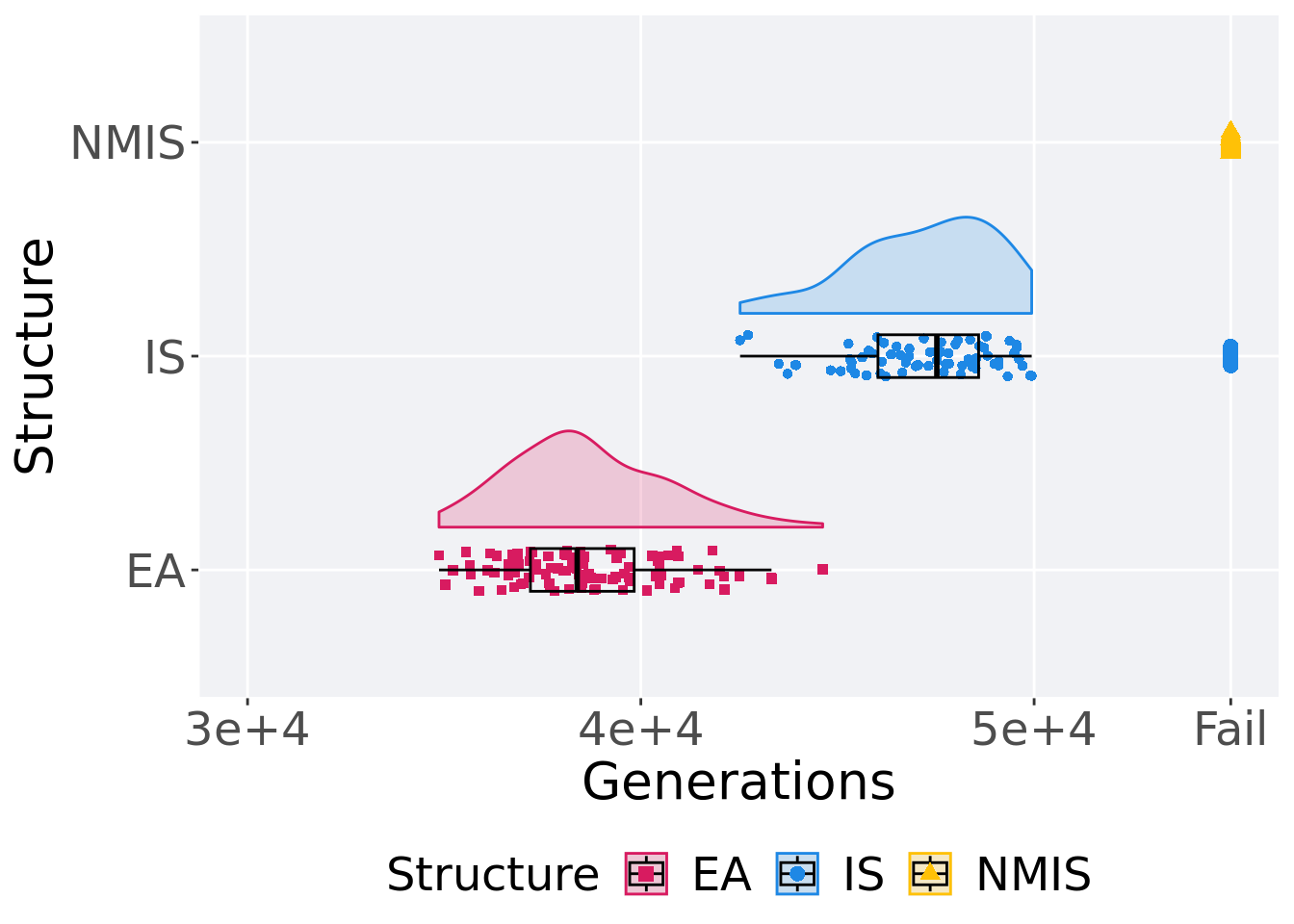
11.4.4.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the first generation a satisfactory solution is found.
ssf = filter(mi50_ssf, Diagnostic == 'ORDERED_EXPLOITATION' & `Selection\nScheme` == 'LEXICASE' & Generations < 60000)
ssf %>%
group_by(Structure) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(Generations)),
min = min(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(Generations, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(Generations, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 2 x 8
## Structure count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 EA 100 0 34868 38382. 38649. 44624 2638.
## 2 IS 70 0 42523 47526. 47195. 49938 2560.Kruskal–Wallis test provides evidence of difference among selection schemes.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: Generations by Structure
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 122.11, df = 1, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = ssf$Generations, g = ssf$Structure, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'g')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: ssf$Generations and ssf$Structure
##
## EA
## IS <2e-16
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni