Chapter 4 Contradictory objectives results
Here we present the results for activation gene coverage and satisfactory trait coverage found by each selection scheme on the contradictory objectives diagnostic with valley crossing integrated. 50 replicates are conducted for each scheme explored.
4.1 Data setup
DIR = paste(DATA_DIR,'CONTRADICTORY_OBJECTIVES/', sep = "", collapse = NULL)
over_time_df <- read.csv(paste(DIR,'over-time.csv', sep = "", collapse = NULL), header = TRUE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
over_time_df$uni_str_pos = over_time_df$uni_str_pos + over_time_df$arc_acti_gene - over_time_df$overlap
over_time_df$scheme <- factor(over_time_df$scheme, levels = NAMES)
over_time_df$acro <- factor(over_time_df$acro, levels = ACRO)
best_df <- read.csv(paste(DIR,'best.csv', sep = "", collapse = NULL), header = TRUE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
best_df$acro <- factor(best_df$acro, levels = ACRO)4.2 Activation gene coverage over time
Activation gene coverage in a population over time. Data points on the graph is the average activation gene coverage across 50 replicates every 2000 generations. Shading comes from the best and worse coverage across 50 replicates.
lines = over_time_df %>%
group_by(scheme, gen) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
min = min(uni_str_pos),
mean = mean(uni_str_pos),
max = max(uni_str_pos)
)## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'scheme'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.lines$scheme <- factor(lines$scheme, levels = c('Truncation (tru)','Tournament (tor)','Lexicase (lex)','Random (ran)','Genotypic Fitness Sharing (gfs)','Phenotypic Fitness Sharing (pfs)','Nondominated Sorting (nds)','Novelty Search (nov)'))
over_time_plot = ggplot(lines, aes(x=gen, y=mean, group = scheme, fill = scheme, color = scheme, shape = scheme)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = min, ymax = max), alpha = 0.1) +
geom_line(size = 0.5) +
geom_point(data = filter(lines, gen %% 2000 == 0 & gen != 0), size = 1.5, stroke = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Coverage",
limits=c(0, 100.1),
breaks=seq(0,100, 20),
labels=c("0", "20", "40", "60", "80", "100")
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(0, 50000),
breaks=c(0, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000),
labels=c("0e+4", "1e+4", "2e+4", "3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4")
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=c(5,3,1,20,2,6,0,4))+
scale_colour_manual(values = c('#332288','#88CCEE','#EE7733','#CCBB44','#EE3377','#117733','#882255','#44AA99')) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c('#332288','#88CCEE','#EE7733','#CCBB44','#EE3377','#117733','#882255','#44AA99')) +
ggtitle('Activation gene coverage over time')+
p_theme +
guides(
shape=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme'),
color=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme'),
fill=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme')
)
over_time_plot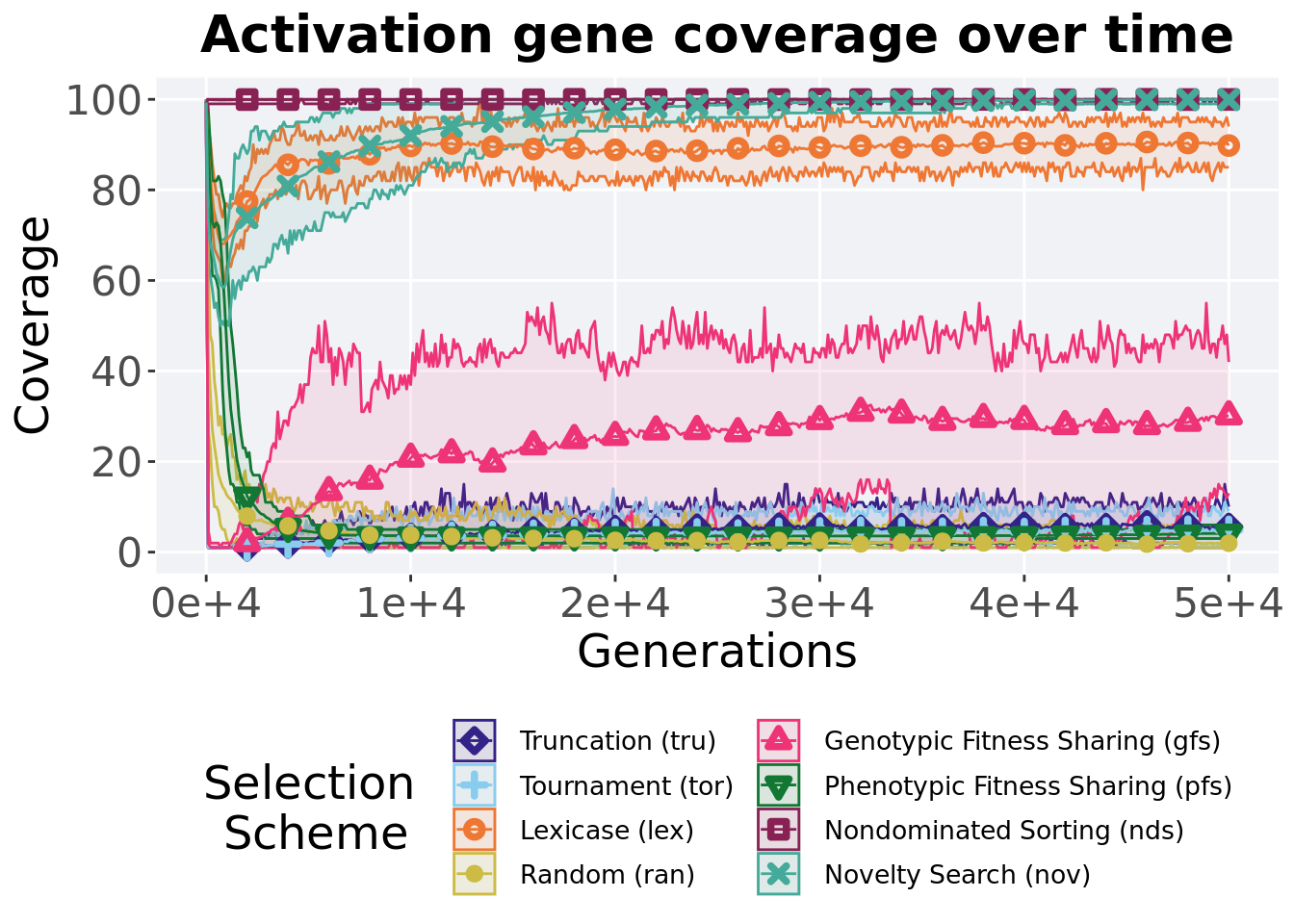
4.3 Final activation gene coverage
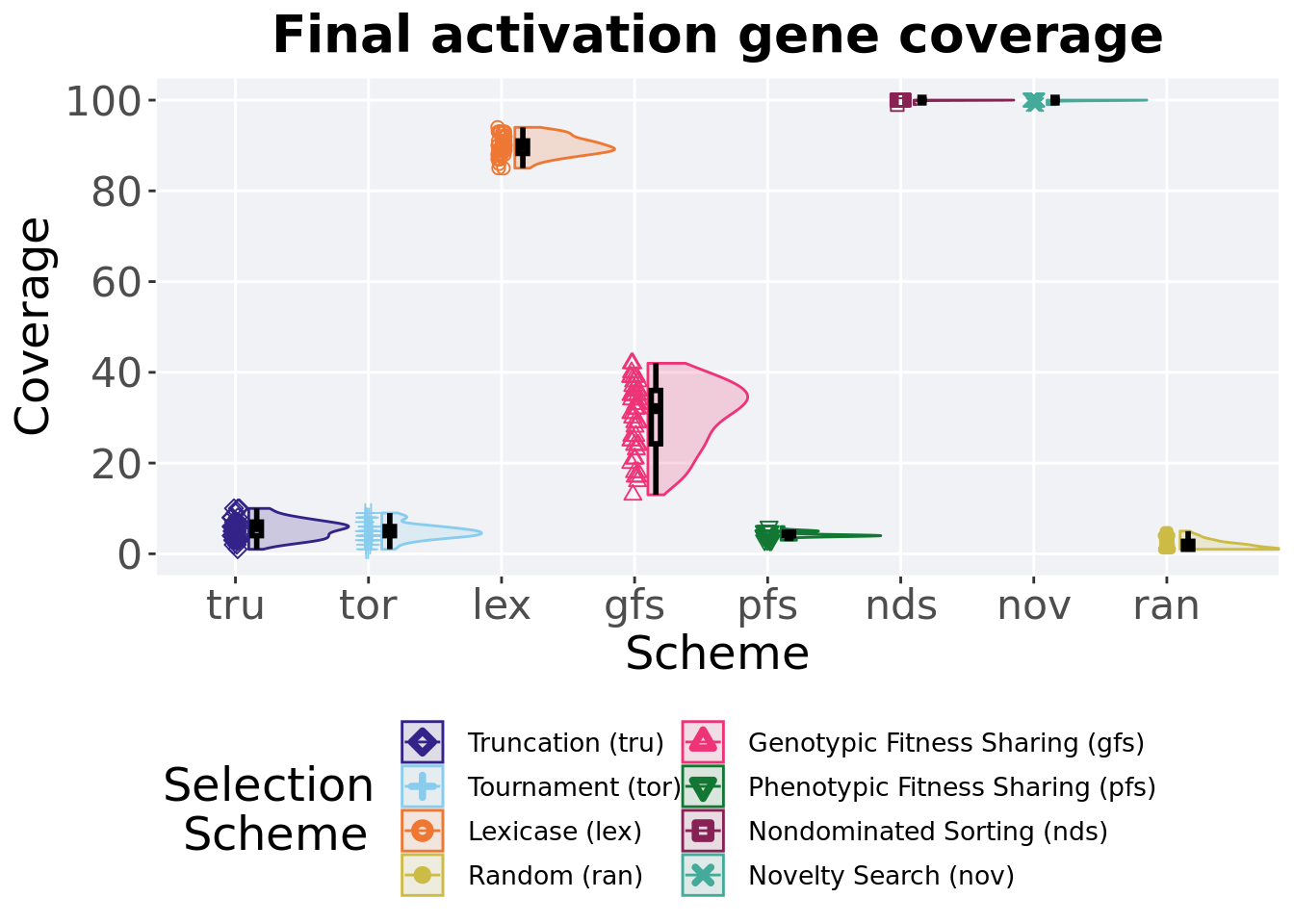
Activation gene coverage found in the final population at 50,000 generations.
plot = filter(over_time_df, gen == 50000) %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = acro, y = uni_str_pos, color = acro, fill = acro, shape = acro)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .1, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2, width = 1.5) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .07, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0, size = 1.0, position = position_nudge(x = .16, y = 0)) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = 0.03, height = 0.02), size = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Coverage",
limits=c(0, 100.1),
breaks=seq(0,100, 20),
labels=c("0", "20", "40", "60", "80", "100")
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Scheme"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Final activation gene coverage')+
p_theme
plot_grid(
plot +
theme(legend.position="none"),
legend,
nrow=2,
rel_heights = c(3,1)
)
4.3.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the coverage found in the final population.
act_coverage = filter(over_time_df, gen == 50000)
act_coverage$acro = factor(act_coverage$acro, levels = c('nds','nov','lex','gfs','tru','tor','pfs','ran'))
act_coverage %>%
group_by(acro) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(uni_str_pos)),
min = min(uni_str_pos, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(uni_str_pos, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(uni_str_pos, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(uni_str_pos, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(uni_str_pos, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 8 x 8
## acro count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 nds 50 0 99 100 100. 100 0
## 2 nov 50 0 99 100 99.9 100 0
## 3 lex 50 0 85 90 89.8 94 2.75
## 4 gfs 50 0 13 32 30.1 42 11.8
## 5 tru 50 0 1 6 5.5 10 3
## 6 tor 50 0 1 5 4.86 9 2
## 7 pfs 50 0 3 4 4.18 6 0.75
## 8 ran 50 0 1 2 1.96 5 1.75Kruskal–Wallis test illustrates evidence of statistical differences.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: uni_str_pos by acro
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 369.27, df = 7, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = act_coverage$uni_str_pos, g = act_coverage$acro, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'l')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: act_coverage$uni_str_pos and act_coverage$acro
##
## nds nov lex gfs tru tor pfs
## nov 1.0000 - - - - - -
## lex < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - - - -
## gfs < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - - -
## tru < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - -
## tor < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 1.0000 - -
## pfs < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 0.0095 0.1827 -
## ran < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 1.7e-12 1.3e-11 5.0e-13
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni4.4 Satisfactory trait coverage over time
Satisfactory trait coverage in a population over time. Data points on the graph is the average activation gene coverage across 50 replicates every 2000 generations. Shading comes from the best and worse coverage across 50 replicates.
lines = over_time_df %>%
group_by(scheme, gen) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
min = min(pop_uni_obj),
mean = mean(pop_uni_obj),
max = max(pop_uni_obj)
)## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'scheme'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.lines$scheme <- factor(lines$scheme, levels = c('Truncation (tru)','Tournament (tor)','Lexicase (lex)','Random (ran)','Genotypic Fitness Sharing (gfs)','Phenotypic Fitness Sharing (pfs)','Nondominated Sorting (nds)','Novelty Search (nov)'))
over_time_plot = ggplot(lines, aes(x=gen, y=mean, group = scheme, fill = scheme, color = scheme, shape = scheme)) +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = min, ymax = max), alpha = 0.1) +
geom_line(size = 0.5) +
geom_point(data = filter(lines, gen %% 2000 == 0 & gen != 0), size = 1.5, stroke = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Coverage"
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name="Generations",
limits=c(0, 50000),
breaks=c(0, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000),
labels=c("0e+4", "1e+4", "2e+4", "3e+4", "4e+4", "5e+4")
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=c(5,3,1,20,2,6,0,4))+
scale_colour_manual(values = c('#332288','#88CCEE','#EE7733','#CCBB44','#EE3377','#117733','#882255','#44AA99')) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c('#332288','#88CCEE','#EE7733','#CCBB44','#EE3377','#117733','#882255','#44AA99')) +
ggtitle('Satisfactory trait coverage over time')+
p_theme +
guides(
shape=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme'),
color=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme'),
fill=guide_legend(ncol=2, title.position = "left", title = 'Selection \nScheme')
)
over_time_plot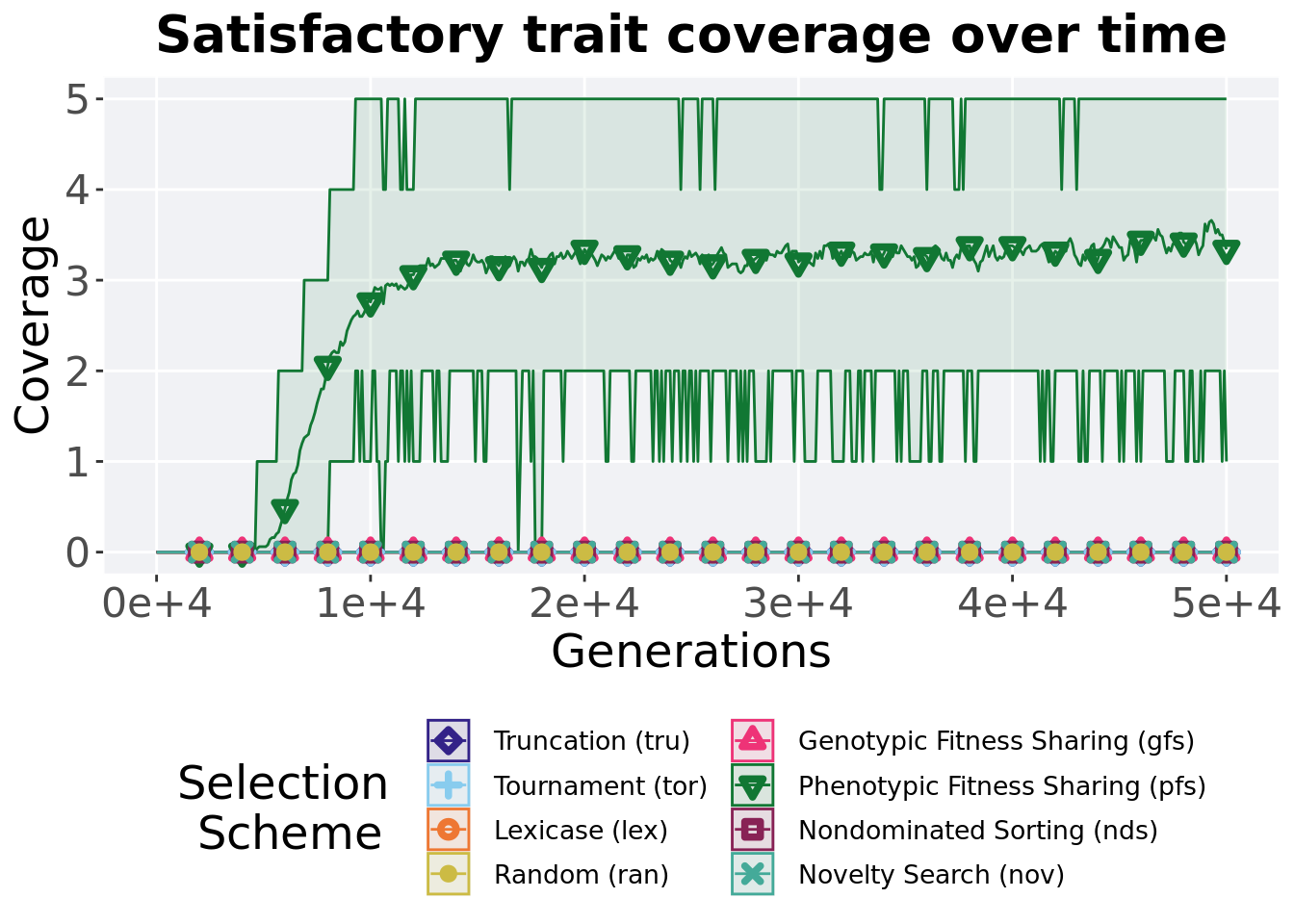
4.5 Final satisfactory trait coverage
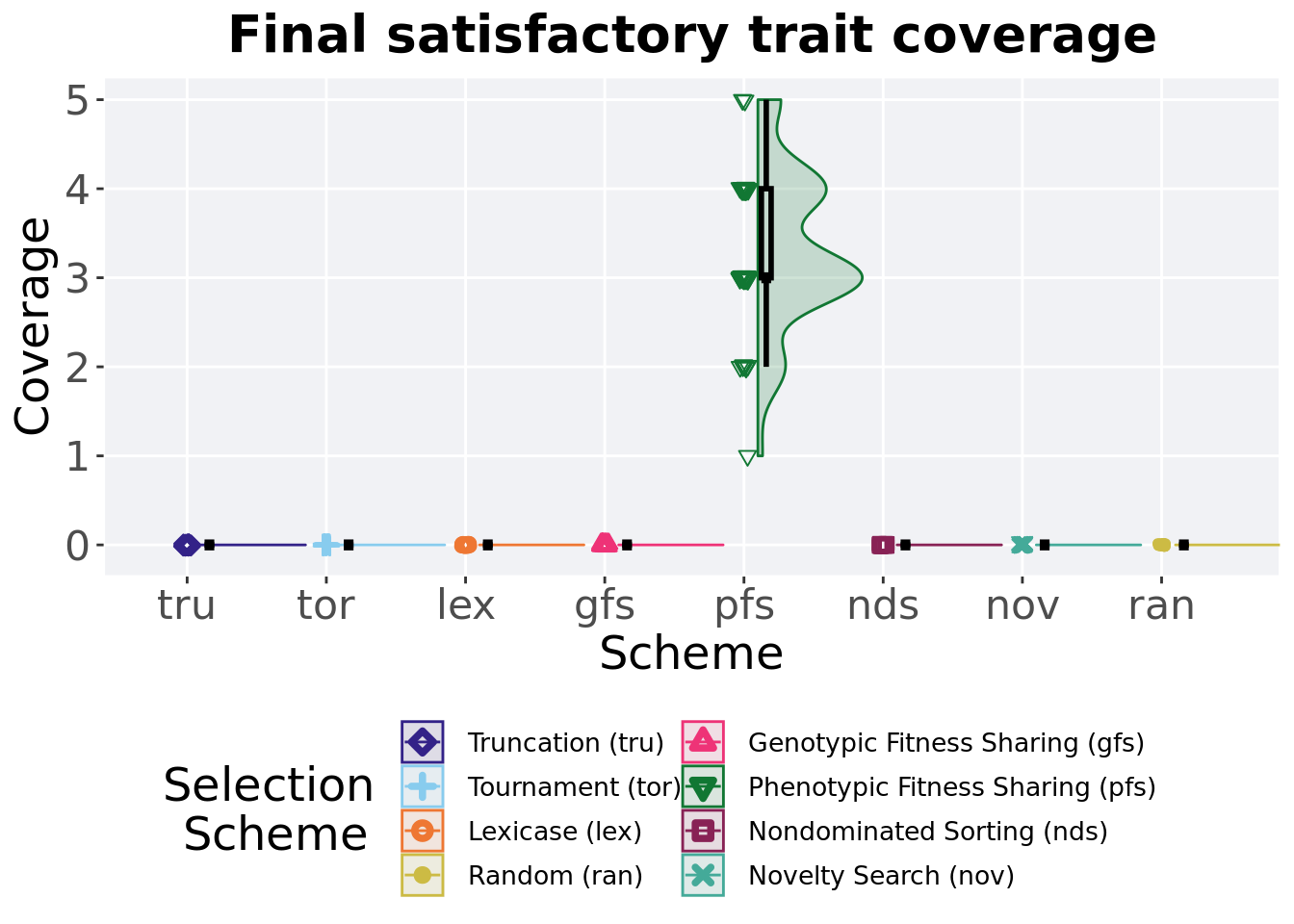
Satisfactory trait coverage found in the final population at 50,000 generations.
plot = filter(over_time_df, gen == 50000) %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = acro, y = pop_uni_obj, color = acro, fill = acro, shape = acro)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .1, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2, width = 1.5) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .07, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0, size = 1.0, position = position_nudge(x = .16, y = 0)) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = 0.03, height = 0.02), size = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Coverage",
limits=c(-0.1, 5)
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Scheme"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Final satisfactory trait coverage')+
p_theme
plot_grid(
plot +
theme(legend.position="none"),
legend,
nrow=2,
rel_heights = c(3,1)
)
4.5.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the coverage found in the final population.
act_coverage = filter(over_time_df, gen == 50000)
act_coverage$acro = factor(act_coverage$acro, levels = c('pfs','nds','lex','gfs','tor','tru','nov','ran'))
act_coverage %>%
group_by(acro) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(pop_uni_obj)),
min = min(pop_uni_obj, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(pop_uni_obj, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(pop_uni_obj, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(pop_uni_obj, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(pop_uni_obj, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 8 x 8
## acro count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
## 1 pfs 50 0 1 3 3.34 5 1
## 2 nds 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 3 lex 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 4 gfs 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 5 tor 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 6 tru 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 7 nov 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
## 8 ran 50 0 0 0 0 0 0Kruskal–Wallis test illustrates evidence of statistical differences.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: pop_uni_obj by acro
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 396.94, df = 7, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = act_coverage$pop_uni_obj, g = act_coverage$acro, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'l')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: act_coverage$pop_uni_obj and act_coverage$acro
##
## pfs nds lex gfs tor tru nov
## nds <2e-16 - - - - - -
## lex <2e-16 1 - - - - -
## gfs <2e-16 1 1 - - - -
## tor <2e-16 1 1 1 - - -
## tru <2e-16 1 1 1 1 - -
## nov <2e-16 1 1 1 1 1 -
## ran <2e-16 1 1 1 1 1 1
##
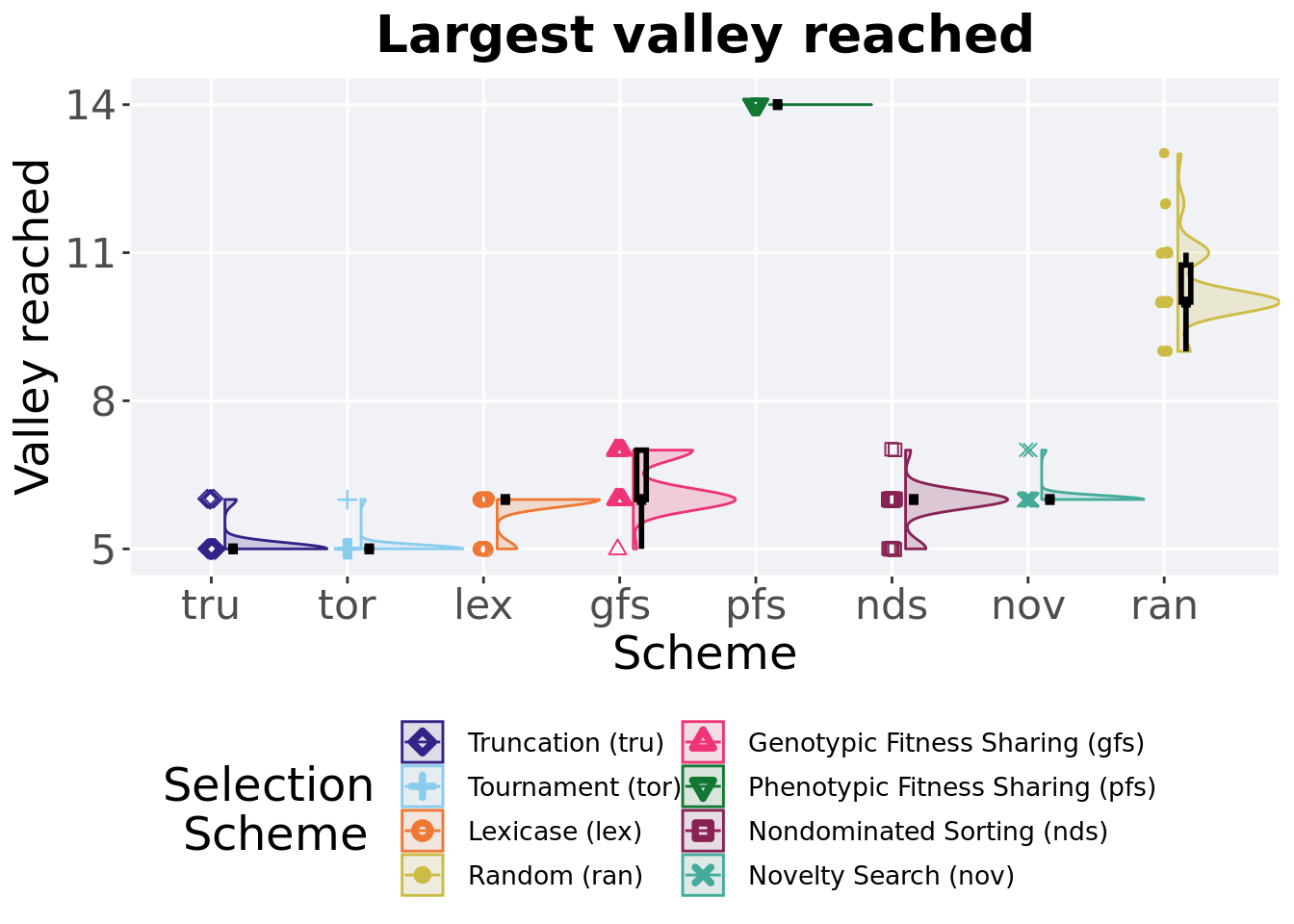
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni4.6 Largest valley reached throughout
The largest valley reached in a single trait throughout an entire evolutionary run. To collect this value, we look through all the best-performing solutions each generation and find the largest valley reached.
plot = filter(best_df, var == 'ele_big_peak') %>%
ggplot(., aes(x = acro, y = val, color = acro, fill = acro, shape = acro)) +
geom_flat_violin(position = position_nudge(x = .1, y = 0), scale = 'width', alpha = 0.2, width = 1.5) +
geom_boxplot(color = 'black', width = .07, outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.0, size = 1.0, position = position_nudge(x = .16, y = 0)) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(width = 0.03, height = 0.02), size = 2.0, alpha = 1.0) +
scale_y_continuous(
name="Valley reached",
limits=c(4.9,14.1),
breaks=c(5,8,11,14)
) +
scale_x_discrete(
name="Scheme"
)+
scale_shape_manual(values=SHAPE)+
scale_colour_manual(values = cb_palette, ) +
scale_fill_manual(values = cb_palette) +
ggtitle('Largest valley reached')+
p_theme
plot_grid(
plot +
theme(legend.position="none"),
legend,
nrow=2,
rel_heights = c(3,1)
)
4.6.1 Stats
Summary statistics for the largest valley crossed.
valleys = filter(best_df, var == 'ele_big_peak')
valleys$acro = factor(valleys$acro, levels = c('pfs','ran','gfs','nov','nds','lex','tru','tor'))
valleys %>%
group_by(acro) %>%
dplyr::summarise(
count = n(),
na_cnt = sum(is.na(val)),
min = min(val, na.rm = TRUE),
median = median(val, na.rm = TRUE),
mean = mean(val, na.rm = TRUE),
max = max(val, na.rm = TRUE),
IQR = IQR(val, na.rm = TRUE)
)## # A tibble: 8 x 8
## acro count na_cnt min median mean max IQR
## <fct> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 pfs 50 0 14 14 14 14 0
## 2 ran 50 0 9 10 10.3 13 0.75
## 3 gfs 50 0 5 6 6.34 7 1
## 4 nov 50 0 6 6 6.04 7 0
## 5 nds 50 0 5 6 5.88 7 0
## 6 lex 50 0 5 6 5.84 6 0
## 7 tru 50 0 5 5 5.1 6 0
## 8 tor 50 0 5 5 5.04 6 0Kruskal–Wallis test illustrates evidence of statistical differences.
##
## Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test
##
## data: val by acro
## Kruskal-Wallis chi-squared = 352.03, df = 7, p-value < 2.2e-16Results for post-hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Bonferroni correction.
pairwise.wilcox.test(x = valleys$val, g = valleys$acro, p.adjust.method = "bonferroni",
paired = FALSE, conf.int = FALSE, alternative = 'l')##
## Pairwise comparisons using Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: valleys$val and valleys$acro
##
## pfs ran gfs nov nds lex tru
## ran < 2e-16 - - - - - -
## gfs < 2e-16 < 2e-16 - - - - -
## nov < 2e-16 < 2e-16 0.00347 - - - -
## nds < 2e-16 < 2e-16 0.00018 0.26915 - - -
## lex < 2e-16 < 2e-16 1.3e-05 0.01917 1.00000 - -
## tru < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 2.8e-12 2.3e-12 -
## tor < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 < 2e-16 2.2e-14 1.6e-14 1.00000
##
## P value adjustment method: bonferroni